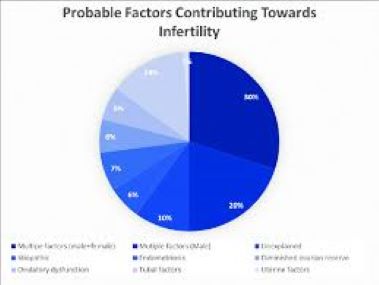
Major Contributors To Rising Infertility

Srinagar- Late marriages, lack of awareness about contraception, rising obesity and changes in lifestyle are some of the leading Major Contributors To Rising Infertility in Jammu and Kashmir, especially among women, according to doctors.
Dr Barjasta Bahar, a prominent gynecologist at the District Hospital Srinagar (DHSK) said that there are several key reasons behind the growing infertility crisis in the region.
She said one of the most significant contributors is late marriage. As women marry at older ages, the natural fertility window begins to decline, making it more difficult for them to conceive, she said.
“The peak fertility age for women is between 18 and 25 years, Major Contributors To Rising Infertility but many women today are getting married in their late 20s or even in their 30s, by which time there is a notable decline in fertility,” said Dr Bahar. She further explained that social factors such as poverty, unemployment, dowry pressures, extravagant wedding traditions, delayed access to higher education, and a long wait for government jobs contribute to this delay in marriage.
In addition to delayed marriages, Dr Bahar said that Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS), a common hormonal disorder among women of reproductive age, is also contributing to the rise in infertility cases.
Major Contributors to Rising Infertility
“Obesity, lifestyle changes, poor eating habits and rising rates of diabetes are other key factors playing a role in the decline of fertility,” she said. “We need to create a societal awareness system that encourages timely marriages, healthy eating habits, and weight management. Major Contributors To Rising Infertility, these changes can significantly reduce the risk of infertility.”
Dr Rukhsana, another gynaecologist, said that Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID), an infection of the reproductive organs, is another serious issue contributing to infertility. PID, often caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia and gonorrhoea, can lead to long-term complications, including infertility. Major Contributors To Rising Infertility, she also cited an increase in unsafe abortions, particularly those conducted by untrained individuals, which can result in infections and long-lasting reproductive damage.
“Septic abortions are a major cause of infertility, especially when performed by unqualified practitioners. These infections can permanently damage the reproductive organs,” Dr Rukhsana explained.
Moreover, a lack of awareness about contraception and reproductive health remains a major challenge in the region, contributing to unintended pregnancies, unsafe abortions, and, ultimately, infertility.
Environmental Toxins and Pollutants
a. Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals (EDCs)
EDCs are substances found in many everyday products, including plastics, cosmetics, and pesticides, that can interfere with the body’s hormone systems. Chemicals like bisphenol A (BPA), phthalates, and parabens mimic hormones, potentially disrupting natural hormone cycles critical for reproduction. Research has shown that exposure to these chemicals can lead to lower sperm counts, abnormal sperm morphology, and reduced fertility in women by impacting ovarian function.
b. Heavy Metals Exposure
Exposure to heavy metals, such as lead, mercury, and cadmium, is associated with infertility. These metals accumulate in the body and cause oxidative stress, which damages reproductive cells and tissues. Men exposed to heavy metals often experience decreased sperm quality, while women may suffer from menstrual irregularities and ovarian dysfunction.
c. Air Pollution
Air pollution has been shown to have detrimental effects on fertility in both men and women. Studies have found Major Contributors To Rising Infertility that exposure to pollutants like fine particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen dioxide, and sulfur dioxide can impair reproductive health. Pollutants can cause oxidative stress, leading to reduced sperm motility and damage to the reproductive organs. Women exposed to high levels of air pollution may face challenges such as reduced ovarian reserve and hormonal disruptions, leading to difficulties in conception.
Doctors said that obesity, sedentary lifestyles, excessive consumption of junk food, and the tendency to delay childbearing in favour of career or economic stability are all interconnected factors fueling the infertility trend.
“An appropriate age for marriage, better education on reproductive health, a balanced lifestyle, and regular exercise are essential to reverse the infertility trend in the region,” the doctors stressed.
Age-Related Decline in Fertility
a. Delayed Parenthood
The trend of delaying parenthood has significantly contributed to rising infertility rates. Many individuals now pursue education, careers, and personal goals before starting a family, often resulting in conception attempts later in life. Female fertility typically begins to decline after the age of 30 and accelerates after 35 due to a decrease in both the quantity and quality of eggs. Similarly, male fertility also declines with age, as sperm quality deteriorates over time.
b. Biological Aging of Reproductive Cells
As women age, the likelihood of chromosomal abnormalities in eggs increases, making conception more difficult and raising the risk of miscarriage and congenital disabilities. In men, aging contributes to decreased testosterone levels, reduced sperm motility, and an increased likelihood of genetic mutations in sperm, which can impact fertility outcomes.
4. Medical Conditions Affecting Fertility
a. Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS)
PCOS is one of the leading causes of infertility in women. This hormonal disorder causes irregular ovulation, excessive androgen production, and the formation of cysts on the ovaries. The condition disrupts the normal menstrual cycle and can make it difficult for women to conceive without medical intervention. Additionally, women with PCOS often have insulin resistance, which further impacts fertility by altering hormone levels.
b. Endometriosis
Endometriosis is a condition where the tissue similar to the uterine lining grows outside the uterus, causing inflammation, pain, and often, fertility issues. This condition can damage the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and the uterus itself, making it harder for fertilization to occur and for embryos to implant successfully. Endometriosis affects approximately 10% of women of reproductive age, and its prevalence is rising, contributing to increased rates of infertility.
According to the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) 2019-21, Jammu and Kashmir has the lowest fertility rate in India, with a decline of 0.6 percent since the last survey conducted in 2015-16. Major Contributors To Rising Infertility, this reflects a wider trend of delayed childbearing and increasing infertility in the state. essentials overview etiology of infertility.
Experts are urging a multi-pronged approach that includes education, early marriages, healthier lifestyles, and greater access to reproductive health services to curb the rising infertility rates in the region.